test for interosse membrane tear|High Ankle Sprains : convenience store The Syndesmosis Squeeze Test of the ankle is a common orthopedic test to assess for syndesmosis injuries at the ankle after inversion trauma. web14 de nov. de 2020 · 35. 4.5K views 2 years ago MAR AZUL. Aprenda a jogar Batalha Naval; já ouviu falar? (rs) Apesar de ser um jogo tão conhecido, o vídeo foi um dos .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBThe latest tweets from @svscomics
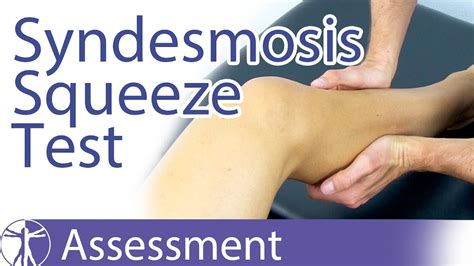
The Syndesmosis Squeeze Test
High Ankle Sprain & Syndesmosis Injuries are traumatic injuries that affect the distal tibiofibular ligaments and most commonly occur due to sudden external rotation of the ankle. Diagnosis is suspected clinically with .The Syndesmosis Squeeze Test of the ankle is a common orthopedic test to assess for syndesmosis injuries at the ankle after inversion trauma. Diagnosis can be difficult. Clinicians should consider the possibility of syndesmotic injury in athletes with pain or injury around the ankle or lower leg. Treatment too is different . interosseous membrane injury 6. MRI. MRI has been shown to accurately detect injuries to the ligamentous structures of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis 1-3. The anterior .
1. Dorsiflexion External Rotation Stress Test (Kleiger's Test) Determines rotator damage to the deltoid ligament or the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Performed by having the knee flexed by 90 degrees with the ankle in neutral position and . The MRI is a better diagnostic tool for looking at soft tissue injuries including ligament and interosseous membrane tears. Who gets a high ankle sprain? The incidence of .
custom general pin type moisture meter
Complete tear of the AITFL with interosseous ligament sprain in a 22 year old male after wakeboarding injury. (12a) Axial fast spin-echo T2-weighted image demonstrates complete AITFL tear. The torn ligament fibers are clumped into .Tests for a syndesmosis injury external rotation stress test, squeeze test and interosseous membrane tenderness length should be performed if the mechanism suggests a syndesmosis . Radiological and CT examination are an important basis for diagnosing ankle syndesmosis injury. Physical examination combined with MRI to determine the damage to the interosseous membrane is significant in guiding .tear Figure 1. Lateral ankle ligaments Reproduced from Brukner P, Kahn K. Clinical sports medicine, 3rd edn. Sydney: McGraw-Hill, 2007 . external rotation stress test, squeeze test and interosseous membrane tenderness length should be performed if the mechanism suggests a syndesmosis injury, or if there is tenderness on palpation of the AitFl
Large sustained loads occur after radial head resection with concurrent interosseous membrane tears, resulting in the proximal migration of the radius and disruption of the distal radioulnar joint. Ultimately, the treatment option for severe membrane disruption combined with proximal migration of the radius is the creation of a single bone forearm.TESTS. POSITION OF THE ANKLE. STRUCTURES INVOLVED. . Interosseous Membrane. Knee is flexed 90 0 and gastrocnemius is relaxed. Move the calcaneus and talus to each side as a unit. . If this causes pain then must consider a tear of the anterior tibiofibular ligament. Depending on severity the interosseous membrane may be involved. Pain will .
a through forearm rotation and actively transfers forces from the radius to the ulna. The interosseous membrane’s unique functional capabilities result from its anatomic and histologic organization, which produces a stiff structure with elastic properties capable of maintaining large loads. The interosseous membrane’s load transferring ability reduces the forces placed on . The distal tibia and fibula are held tightly together by the syndesmosis membrane, and the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments. A syndesmotic sprain or high ankle sprain is an injury to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis with possible disruption of the distal tibiofibular ligaments and interosseous membrane.The first dorsal interosseous muscle can be tested by placing the patient's palm flat on a table and asking the patient to abduct his/her index finger against the examiner's resistance. The muscle belly can be both seen and palpated and is a reliable test for the ulnar nerve . The interosseous membrane of the leg is also referred to as the middle tibiofibular ligament. This ligament extends through the fibula and tibia’s interosseous crests and separates the muscles .
As this tear progresses up the interosseous membrane, all the forces are placed more proximally along the fibula at the area where the tear ends, causing a proximal fibula fracture (2). . stress test under fluoroscopy (8). Type of .
Create Group Test Enter Test Code . all acute traumatic TFCC tears. operative. arthroscopic vs. open debridement and/or repair . indications. . Radial head fracture with an interosseous membrane injury extending to DRUJ . unstable relationship between ulna .
Objectives: To correlate interosseous membrane (IOM) tears of the ankle to the height of fibular fractures in operative ankle fractures. Design: Prospective clinical trial. Setting: University Level 1 trauma center. Patients: All patients admitted with a closed operative ankle fracture were included. Of 93 patients originally evaluated, 73 patients had adequate MRI for evaluation. The crural interosseous membrane (IM) extends between the interosseous crests of the tibia and fibula, helps stabilize the tibio-fibular relationship and separates anterior compartment muscles from posterior compartment muscles of the leg.Previous microscopic and anatomical studies of the crural IM have shown the angulation of fibers,1,2 diameter of IM fiber .Background: Injuries of the interosseous membrane (IOM) of the forearm are frequently unrecognized, difficult to treat, and can result in a devastating sequelae for the wrist and elbow. Purpose: The purpose of this review article is to evaluate the dignosis, biomechanics, clinical results, and propose a treatment approach to this rare complex entity.
Syndesmotic ankle injury (high ankle sprain)
Objectives . To correlate interosseous membrane (IOM) tears of the ankle to the height of fibular fractures in operative ankle fractures.. Design . Prospective clinical trial. Setting . University Level 1 trauma center. Patients . All patients admitted with a .During preparation of the specimens, when only half the interosseous membrane had been divided, performance of the test was not found to produce any noticeable increase in the size of the tear. Discussion These results suggest that the radius joystick test may be used for the intra-operative diagnosis of interosseous membrane disruption and .
Injury to the interosseous membrane of the forearm typically occurs in conjunction with disruption of the radial head and the distal radioulnar joint. Frequently, the true extent of injury is not initially appreciated, and patients may develop . Book consulting time with me: https://www.footdoctorzach.com/consultFREE Updated shoe anatomy guide: https://geni.us/freeshoeguideFREE Shoelace guide: https:. Nakamura et al 19 suggested that the interosseous membrane was taut in neutral or slight supination and relaxed in maximal supination or pronation, based on a magnetic resonance imaging study that passively . Purpose In the last two decades, a strong interest on the interosseous membrane (IOM) has developed. Methods The authors present a review of the new concepts regarding the understanding of forearm physiology and pathology, with current trends in the surgical management of these rare and debilitating injuries. Results Anatomical and biomechanical .
This essay was 100% sensitive for the detection of this lesion and the positive predictive value was 90%. A study of this test in vivo has not yet been done. 17 The authors believe that the ulnar drawer test also has an accuracy of close to 100%, and that the combination of these two tests would probably increase the certainty of the diagnosis. The Interosseous membrane is a strong fibrous sheet of connective tissue that acts as a long ligamentous membrane between two bones, also known as a syndesmosis joint. These membranes travel from proximal (high) to distal (lower) in an oblique direction and create a natural anatomical divider between the compartments of the forearm and lower leg.
interosseous membrane proximal radial ulnar joint Abstract Background Injuries of the interosseous membrane (IOM) of the forearm are fre-quently unrecognized,difficult totreat, and can result in a devastatingsequelaefor the wrist and elbow. Purpose The purpose of this review article is to evaluate the dignosis, biomechanics,
Physical examination combined with MRI to determine the damage to the interosseous membrane is significant in guiding the treatment of ankle syndesmosis injury with interosseous membrane injury. In the past, inserting syndesmosis screws was the gold standard for treating ankle syndesmosis injury. However, there were increasingly more .An interosseous membrane is a thick dense fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the space between two bones, forming a type of syndesmosis joint. [1] Interosseous membranes in the human body: Interosseous membrane of forearm; Interosseous membrane of leg; Gallery.
Injuries of the interosseous membrane (IOM) of the forearm are frequently unrecognized, difficult to treat, and can result in a devastating sequelae for the wrist and elbow. PURPOSE The purpose of this review article is to evaluate the dignosis, biomechanics, clinical results, and propose a treatment approach to this rare complex entity.The interosseous membrane of the forearm is a complex anatomic structure responsible for load sharing and stability of the forearm and distal radioulnar joint. The interosseous membrane consists of 2 components: a thin, flexible membranous component located proximal and distal to a stiff, relatively thick central band. The central band is responsible for significant load transfer . The interosseous membrane consists of several components: there is a membranous portion, a consistently present central band, accessory bands, and a proximal interosseous band. 9, 26 The strong central band arises an average of 7.7 cm to the radial head and inserts 13.7 cm from the olecranon tip.
Syndesmotic Ankle Sprains
Provocation tests: Watson's test "scaphoid shift test" Test is performed by the examiner stabilizing the scaphoid with one hand while using the other hand to move the wrist from ulnar to radial deviation. Positive test: The examiner should feel a significant "clunk" and the pt will experience pain. Decreased range of motion due to pain
Sports ankle injuries Assessment and management
 .jpg)
Assistir Bom Sucesso Temporada 1. Você pode assistir "Bom Sucesso - Temporada 1" no Globoplay em Stream legalmente. 20 Episódios. T1 Ep1 - Episódio 1. T1 Ep2 - Episódio .
test for interosse membrane tear|High Ankle Sprains